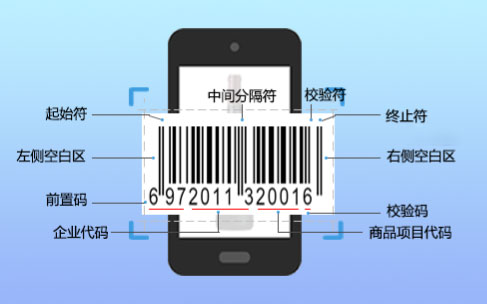
What is a barcode?
A barcode is a graphic identifier that arranges several black bars and blanks with different widths according to certain coding rules to represent a group of information. A common barcode is a pattern of parallel lines arranged by black bars (referred to as bars) and white bars (referred to as blanks) with different reflectivity. Barcodes can mark the country of production, manufacturer, commodity name, production date, book classification number, mailing destination, category, date and many other information, so they are widely used in commodity circulation, book management, postal management, banking system and many other fields. Wrigley Gum was the first bar-coded product.

Uses and Benefits of Barcodes
Use of barcodes:
The barcode is the only "identity card" for goods circulating around the world, and it is the language of international business.
The barcode is an important sign of product traceability;
Barcodes play a role in information transmission in emerging Internet industries;
It has been widely used in e-commerce. From the initial realization of automatic settlement as a commodity ID card to the association and transmission of information throughout the supply chain, it has played a fundamental supporting role in meeting the online and offline integration needs of e-commerce and traditional commerce.
In summary, commodity barcodes have played a huge role in "going to the international market", "tracing food quality and safety", and "e-commerce".
Advantages of barcodes:
Fast input speed: Compared with keyboard input, barcode input speed is several times faster than keyboard input, which can realize "instant data input".
High reliability: keyboard input data error rate is 1%, optical character recognition technology error rate is 1/10000, barcode technology error rate is less than 1/10000.
Can collect a large amount of information: traditional one-dimensional barcodes can collect information of dozens of characters at a time, while two-dimensional barcodes can carry information of thousands of characters, and have certain automatic error correction capabilities.
Flexible and practical: barcode recognition can be used alone as an identification method, or it can be combined with related equipment to form a system to achieve automatic identification, and it can also be connected with other control equipment to achieve automatic management.
In addition, barcode labels are easy to manufacture, have no special requirements for equipment and materials, the identification equipment is easy to operate, does not require special training, and the equipment is relatively cheap. Low cost because the barcode is printed on the product packaging.